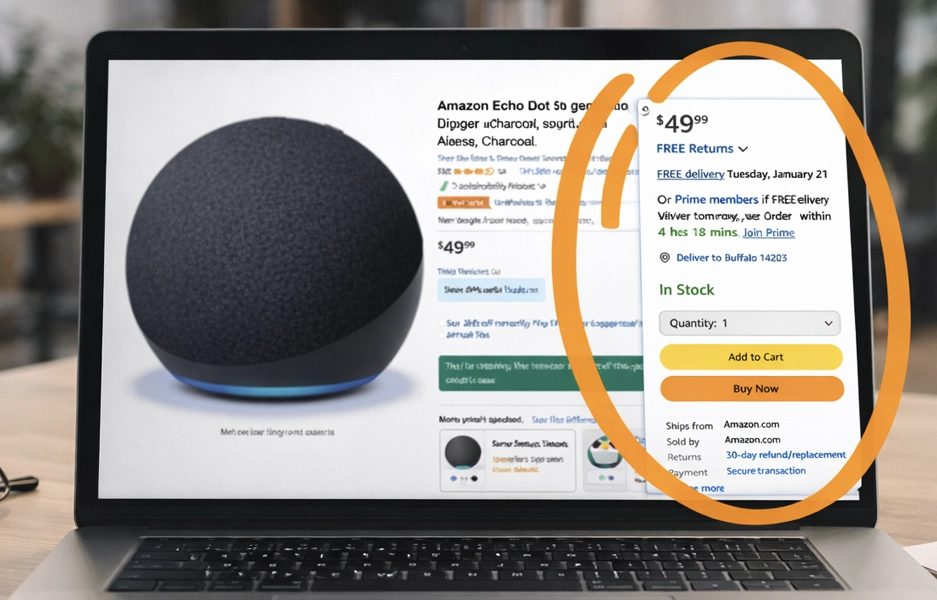
On Amazon, the Buy Box is everything.
If your goal is not just to understand it but to control it, read our complete guide on How to Win the Buy Box on Amazon.
Let’s break down how it works — and why brands often lose control of it.Table of Contents
- What is the Amazon Buy Box?
- Why Choose Brand Alignment's Buy Box Recovery Program?
- Want to Win Back Your Buy Box?
The Amazon Buy Box
The Buy Box (also called the Featured Offer) is the default seller Amazon presents to customers.
When multiple sellers offer the same product on a listing, Amazon rotates the Buy Box among eligible sellers based on performance and pricing factors.
Important to understand:
- Not all sellers are eligible.
- Winning the Buy Box is not permanent.
- It can rotate throughout the day.
- It can be completely suppressed.
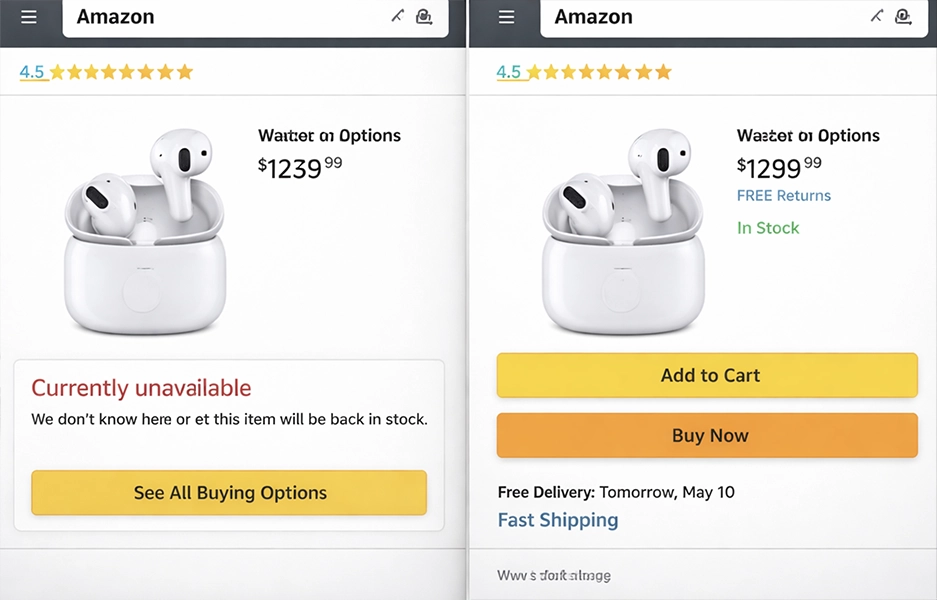
If the Buy Box disappears and only “See All Buying Options” appears, your listing has been suppressed.
How Amazon Decides Who Wins the Buy Box
Amazon’s algorithm evaluates multiple factors simultaneously. The most important include:
1. Landed Price (Not Just Item Price)
Amazon looks at the total cost to the customer, including:
- Product price
- Shipping cost
If your price is above the internal Buy Box threshold (sometimes called the “Landed Price threshold”), you may not even be eligible to win — regardless of performance.
Even if you match the threshold, it does not guarantee ownership. It only makes you eligible.
2. Fulfillment Method
Fulfilled by Amazon (FBA) sellers typically have an advantage because:
- Prime eligibility
- Faster shipping
- Amazon-controlled logistics
However, strong FBM (Fulfilled by Merchant) sellers can still win if metrics are strong and pricing is competitive.
3. Seller Performance Metrics
- Amazon prioritizes sellers with:
- Low Order Defect Rate (ODR)
- Strong on-time shipping
- Low cancellation rates
- High customer satisfaction
Even a small dip in metrics can reduce Buy Box share.
For a better understanding of what brands are missing when visibility drops, read our full guide.
4. Inventory Availability
If you go out of stock, you immediately lose eligibility.
Even worse — if you have inventory but Amazon detects fulfillment or listing issues, you may still lose visibility.
5. External Price Matching
This is where many brands get blindsided.
Amazon enforces price parity across reputable external retailers. If Walmart, Target, or another retailer lists the same SKU at a lower price, Amazon may:
- Raise your Buy Box price threshold
- Suppress the Buy Box entirely
This often results in complete suppression — even when inventory and metrics are strong.
Why Sellers Lose the Buy Box
Losing the Buy Box is rarely random. It typically falls into five categories:
1. Unauthorized Sellers
Grey market sellers often undercut MAP pricing and disrupt pricing stability.
Since Amazon prioritizes competitive pricing, these sellers can capture Buy Box share quickly — even with minimal seller history .
The issue isn’t just lower pricing — it’s supply chain leakage.
2. Authorized Sellers Violating MAP
Even authorized partners violate MAP. In fact, approximately 15% of authorized sellers violate contractual MAP policies.
This creates internal price competition, leading to:
- Price cascading
- Race to the bottom
- Buy Box instability
3. Buy Box Suppression
Sometimes Amazon removes the Buy Box entirely.
This typically happens when:
- External retailers show a lower price
- Amazon’s pricing policy is triggered
- Backend listing issues exist
Suppression means zero visibility — and frozen revenue.
4. Vendor Central vs. Seller Central Conflict
Many brands assume being on Vendor Central protects them.
It does not.
Third-party sellers can still win the Buy Box — even when Amazon Retail is on the listing. Vendor Central may have weighted influence, but it does not guarantee 100% ownership.
5. Inventory Gaps
Arbitrage sellers actively monitor Keepa and similar tools to detect when Amazon or brands go out of stock. They then flood listings and win the Buy Box during those gaps .
This can severely impact:
- Pricing stability
- Review quality
- Brand perception
What Is a “Good” Buy Box Percentage?
It depends on your brand strategy.
- 80–90%+ is common for brands prioritizing control.
- 100% is ideal when protecting brand equity.
- 55–75% may be acceptable if shared with trusted authorized partners.
The real question isn’t the percentage — it’s who is winning it.
If unauthorized sellers are taking share, that’s diverted revenue.
The Hidden Revenue Problem: Inventory Without Visibility
One of the most overlooked issues is this:
You may have inventory in stock… but no Buy Box ownership.
That means:
- Customers can’t easily purchase
- Visibility drops
- Conversion rates collapse
When brands quantify the dollar value of inventory sitting without Buy Box ownership, they often realize the issue is not small — it’s material.
The Three Layers of Buy Box Control
To consistently win the Buy Box, brands need control in three areas:
1. Pricing Discipline
- Enforce MAP policies.
- Monitor external retailers.
- Address price cascading early.
2. Seller Control
- Identify unauthorized sellers.
- Trace supply chain leaks.
- Remove repeat violators.
- Vet new distributors carefully.
Anyone can create a third-party listing. Without marketplace-wide seller monitoring, you are reacting — not controlling.
3. Diagnostics Before Enforcement
Before taking action, brands need clarity:
- Is this external price matching?
- Is this an internal MAP violation?
- Is this inventory-related?
- Is this backend suppression?
Buy Box problems are rarely one-dimensional.
Final Takeaway
The Amazon Buy Box is not random. It is a performance-based, price-sensitive, algorithmic system that rewards:
- Competitive landed pricing
- Strong seller metrics
- Stable fulfillment
- Cross-channel price parity
But for brands, the real issue is not just winning it once — it’s maintaining control over time.
If you’re seeing:
- Declining Buy Box percentage
- Unauthorized sellers appearing
- External price suppression
- Inventory without visibility
It’s not just a listing issue. It’s a marketplace control issue.
Take Control of Your Buy Box
If you’d like to understand what’s specifically affecting your Buy Box performance, our team can help you diagnose the root cause and build a structured recovery plan.